Malta’s economy is set to grow 3.7 per cent in 2023, a downward revision of 0.8 per cent due to a faster-than-expected economic recovery in 2022. As a result, Malta is expected to avoid a recession, with wages set to increase and unemployment set to decline further to three per cent.
By the end of the year, Malta’s economy is set to have grown by 6.8 per cent, an upward revision of 1.8 per cent due to better-than-expected international trade, consumer demand and stable energy prices. Employment is anticipated to increase by 4.9 per cent by the end of 2022, and wages are expected to outpace inflation in later years.
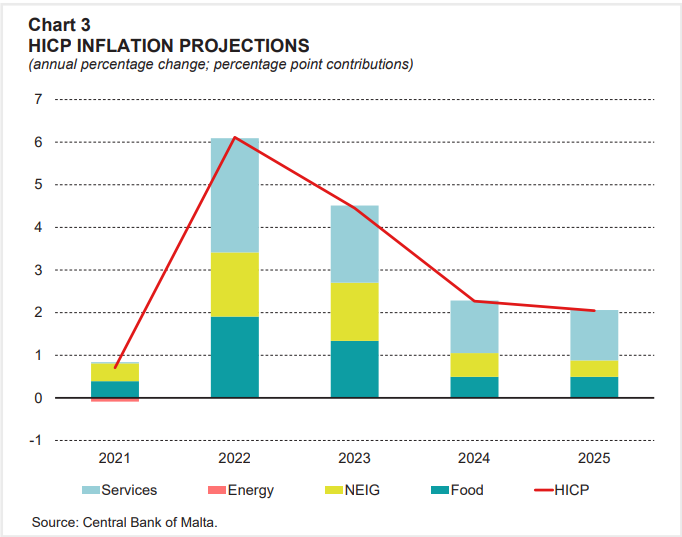
Based on the Harmonised Index of Consumer Prices (HICP), inflation is set to remain high in 2023, reaching 6.1 per cent by the end of this year, going down to 4.5 per cent in 2023, and reaching the European Union’s two per cent target by 2025. High inflation will continue to be driven by historically high importation costs.
The government deficit is anticipated to recede to 5.6 per cent of GDP by the end of the year, compared to 7.8 per cent in 2021, with a further decline to 5.1 per cent in 2023, and down to three per cent of GDP by 2025. This is due to the unwinding of remaining COVID-19 measures, and expected decreases in energy prices, allowing the Government’s debt-to-GDP ratio to remain just under 60 per cent of GDP by 2025, in line with the EU’s Maastricht criteria.
However, the decrease in deficit may not come to pass if the cost of mitigating energy prices is higher than expected, and due to potential state aid expenditure on the national airline.
The biggest risks to Malta’s economic growth for 2023 are a decline in global economic activity which would drive local exports down. Consistently high inflation risks also causing a decrease in both corporate investment and consumer demand. However, these risks may be mitigated by rising wages which may steady local household consumption.

The risks to the current downward trend of inflation may be rising commodity prices due to disruptions of Russian energy supplies, further driving importation and transportation costs, therefore continuing to supersede wage growth.
BNF Bank and Mastercard partner to bring added value to Maltese customers
Collaboration enhances everyday banking through exclusive experiences, rewards, and innovative payment solutions
ĠEMMA launches new podcast series to make financial literacy accessible for all
New episodes will be released every two weeks and will be available across multiple platforms
Malta introduces new 15% tax regime for highly skilled professionals
Qualifying individuals are taxed at a flat 15% rate for an initial five-year period






